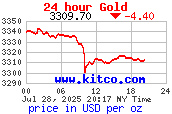
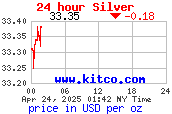
We will never have a perfect model of risk
March 25, 2008
We will never have a perfect model of risk
By Alan Greenspan
Published: March 17 2008 02:00 | Last updated: March 17 2008 02:00
(Financial Times) - The current financial crisis in the US is likely to be judged in retrospect as the most wrenching since the end of the second world war. It will end eventually when home prices stabilise and with them the value of equity in homes supporting troubled mortgage securities...
I do not say that the current systems of risk management or econometric forecasting are not in large measure soundly rooted in the real world. The exploration of the benefits of diversification in risk-management models is unquestionably sound and the use of an elaborate macroeconometric model does enforce forecasting discipline. It requires, for example, that saving equal investment, that the marginal propensity to consume be positive, and that inventories be non-negative. These restraints, among others, eliminated most of the distressing inconsistencies of the unsophisticated forecasting world of a half century ago.
But these models do not fully capture what I believe has been, to date, only a peripheral addendum to business-cycle and financial modelling - the innate human responses that result in swings between euphoria and fear that repeat themselves generation after generation with little evidence of a learning curve. Asset-price bubbles build and burst today as they have since the early 18th century, when modern competitive markets evolved. To be sure, we tend to label such behavioural responses as non-rational. But forecasters' concerns should be not whether human response is rational or irrational, only that it is observable and systematic.
This, to me, is the large missing "explanatory variable" in both risk-management and macroeconometric models. Current practice is to introduce notions of "animal spirits", as John Maynard Keynes put it, through "add factors". That is, we arbitrarily change the outcome of our model's equations. Add-factoring, however, is an implicit recognition that models, as we currently employ them, are structurally deficient; it does not sufficiently address the problem of the missing variable...
In the current crisis, as in past crises, we can learn much, and policy in the future will be informed by these lessons. But we cannot hope to anticipate the specifics of future crises with any degree of confidence. Thus it is important, indeed crucial, that any reforms in, and adjustments to, the structure of markets and regulation not inhibit our most reliable and effective safeguards against cumulative economic failure: market flexibility and open competition.
The writer is former chairman of the US Federal Reserve and author of The Age of Turbulence: Adventures in a New World
Copyright The Financial Times Limited 2008
By Alan Greenspan
Published: March 17 2008 02:00 | Last updated: March 17 2008 02:00
(Financial Times) - The current financial crisis in the US is likely to be judged in retrospect as the most wrenching since the end of the second world war. It will end eventually when home prices stabilise and with them the value of equity in homes supporting troubled mortgage securities...
I do not say that the current systems of risk management or econometric forecasting are not in large measure soundly rooted in the real world. The exploration of the benefits of diversification in risk-management models is unquestionably sound and the use of an elaborate macroeconometric model does enforce forecasting discipline. It requires, for example, that saving equal investment, that the marginal propensity to consume be positive, and that inventories be non-negative. These restraints, among others, eliminated most of the distressing inconsistencies of the unsophisticated forecasting world of a half century ago.
But these models do not fully capture what I believe has been, to date, only a peripheral addendum to business-cycle and financial modelling - the innate human responses that result in swings between euphoria and fear that repeat themselves generation after generation with little evidence of a learning curve. Asset-price bubbles build and burst today as they have since the early 18th century, when modern competitive markets evolved. To be sure, we tend to label such behavioural responses as non-rational. But forecasters' concerns should be not whether human response is rational or irrational, only that it is observable and systematic.
This, to me, is the large missing "explanatory variable" in both risk-management and macroeconometric models. Current practice is to introduce notions of "animal spirits", as John Maynard Keynes put it, through "add factors". That is, we arbitrarily change the outcome of our model's equations. Add-factoring, however, is an implicit recognition that models, as we currently employ them, are structurally deficient; it does not sufficiently address the problem of the missing variable...
In the current crisis, as in past crises, we can learn much, and policy in the future will be informed by these lessons. But we cannot hope to anticipate the specifics of future crises with any degree of confidence. Thus it is important, indeed crucial, that any reforms in, and adjustments to, the structure of markets and regulation not inhibit our most reliable and effective safeguards against cumulative economic failure: market flexibility and open competition.
The writer is former chairman of the US Federal Reserve and author of The Age of Turbulence: Adventures in a New World
Copyright The Financial Times Limited 2008